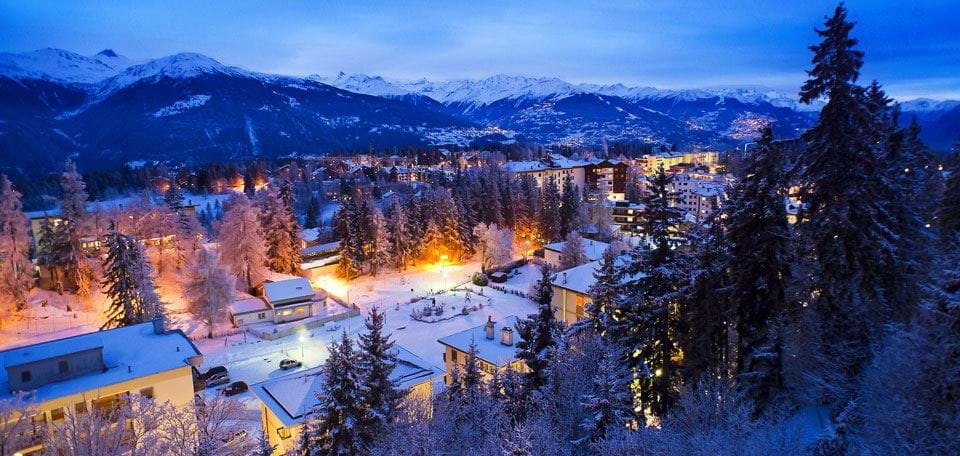
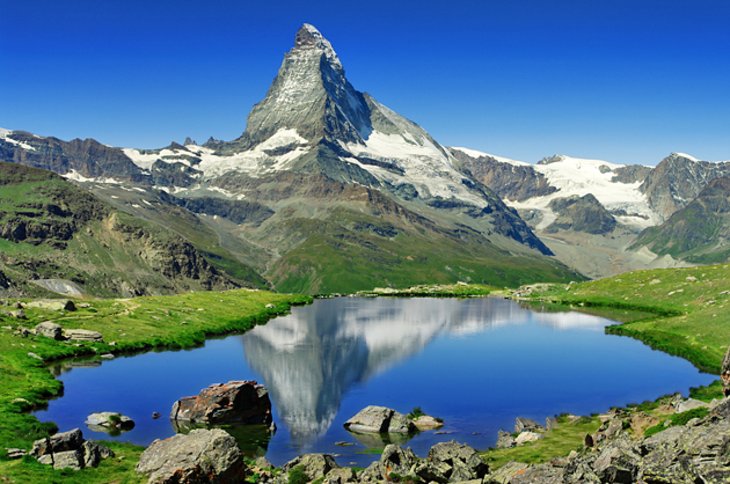
Zermatt was "discovered" by mid-nineteenth-century British mountaineers, most notably Edward Whymper, whose summit of the Matterhorn made the village famous. The Matterhorn was one of the last alpine mountains to be summitted (in 1865), and the first expedition that reached the top ended dramatically with only 3 of the 7 climbers surviving the descent. The story is related in the Matterhorn Museum. Zermatt is a starting point for hikes into the mountains, including the Haute Route that leads to Chamonix in France and the Patrouille des Glaciers. Cable cars and chair lifts carry skiers in the winter and hikers in the summer; the highest of them leads to the Klein Matterhorn at 3,883 m (12,740 ft), a peak on the ridge between Breithorn and Matterhorn that offers extensive views in all directions. It is possible to cross into Italy via the Cervinia cable car station. The year-round population is about 6,000, though there may be several times as many tourists in Zermatt at any one time. Much of the local economy is based on tourism, with about half of the jobs in town in hotels or restaurants and just under half of all apartments are vacation apartments. Just over one-third of the permanent population was born in the town, while another third moved to Zermatt from outside Switzerland.
| Welcome to Switzerland |
|---|
Switzerland VIP services
|

![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
| Start Site | Switzerland jet charters | Switzerland helicopter services | Switzerland luxury cars rental |
|---|
Zermatt VIP services
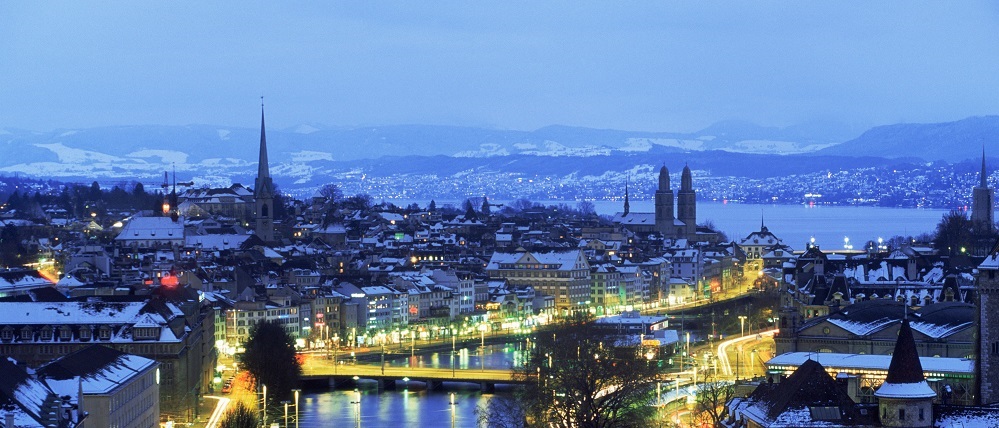
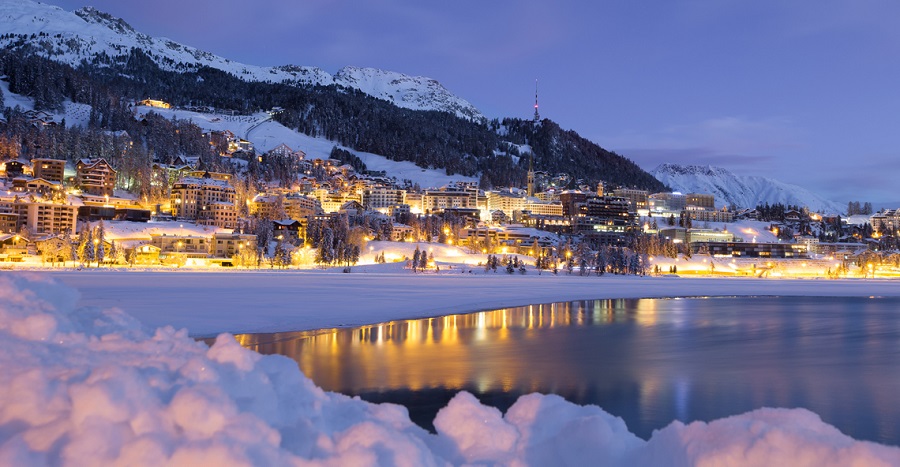
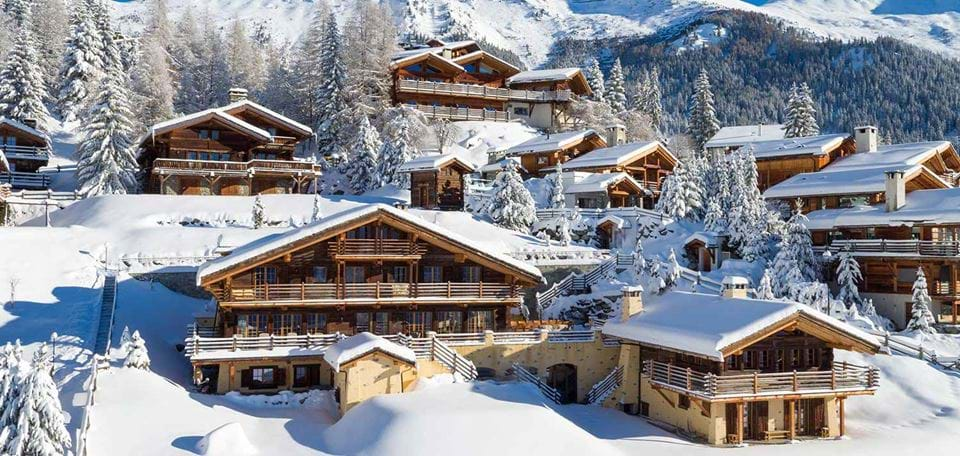
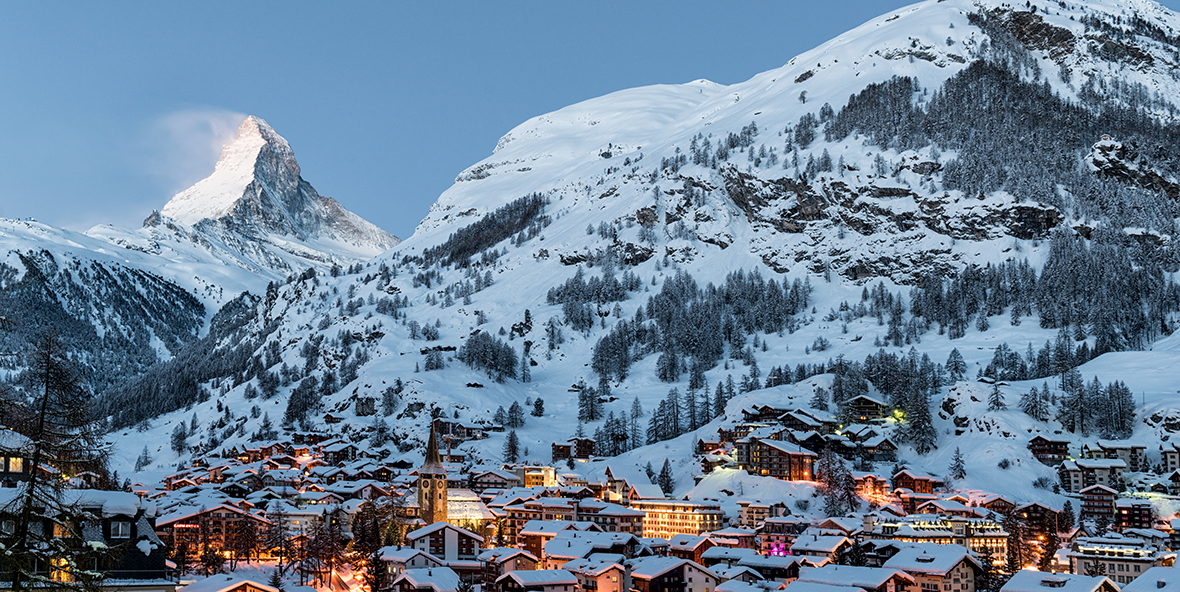
Zermatt, in southern Switzerland’s Valais canton, is a mountain resort renowned for skiing, climbing and hiking. The town, at an elevation of around 1,600m, lies below the iconic, pyramid-shaped Matterhorn peak. Its main street, Bahnhofstrasse is lined with boutique shops, hotels and restaurants, and also has a lively après-ski scene. There are public outdoor rinks for ice-skating and curling.
Zermatt is a municipality in the district of Visp in the German-speaking section of the canton of Valais in Switzerland. It has a population of about 5,800 inhabitants and is classified as a town by the Swiss Federal Statistical Office (FSO).
It lies at the upper end of Mattertal at an elevation of 1,620 m (5,310 ft), at the foot of Switzerland's highest peaks. It lies about 10 km (6.2 mi) from the over 3,292 m (10,801 ft) high Theodul Pass bordering Italy.
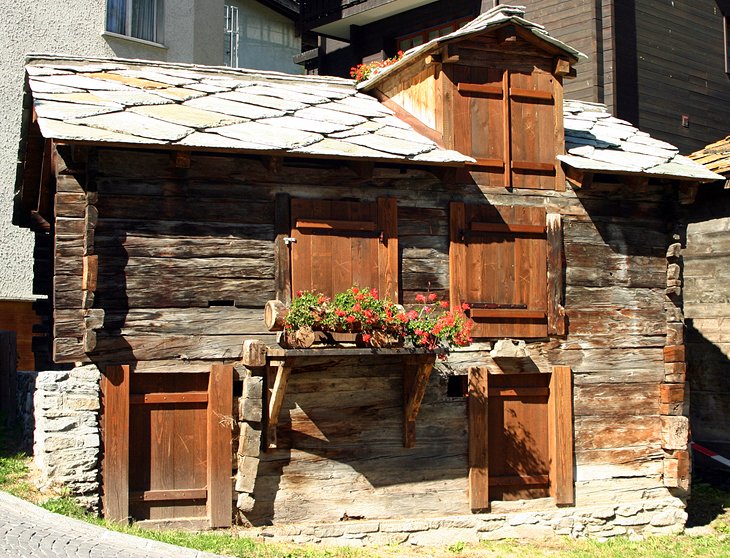
Zermatt is famed as a mountaineering and ski resort of the Swiss Alps. Until the mid-19th century, it was predominantly an agricultural community; the first and tragic ascent of the Matterhorn in 1865 was followed by a rush on the mountains surrounding the village, leading to the construction of many tourist facilities.
Tourism in Zermatt, Switzerland

Best places to visit in Zermatt
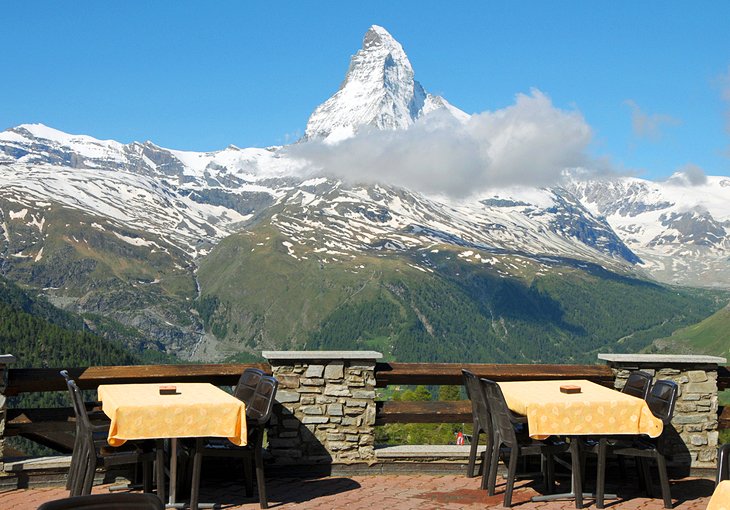
Zermatt is known throughout the world for its skiing, especially Triftji for its moguls. The high altitude results in consistent skiing continuously throughout the summer. Skiing in Zermatt is split up into four areas: Sunnegga, Gornergrat, Klein Matterhorn and Schwarzsee. There is also a connection to Cervinia and Valtournenche in Italy through the Plateau Rosa glacier. The Sunnegga Paradise is accessed via the SunneggaExpress funicular railway, followed by a gondola to Blauherd and finally a cable car onwards to the Rothorn (3,103 m) above. The topography of the mountain and the valley tends to keep the Rothorn clear and sunny, even when Zermatt is submerged in cloud. The Gornergrat is served by the Gornergrat railway, a 29-minute ride to the Gornergrat peak (3,089 m), via Riffelalp, Rotenboden and Riffelberg, (with limited stops at Findelbach and Landtunnel just above Zermatt). At the summit, the hotel and restaurant have been refurbished and accommodate a shopping centre. Riffelalp station is linked to Riffelalp Resort by a short tramway line named Riffelalptram. Near the southern end of Zermatt, the Matterhorn Express gondola transports passengers up to the interchange station at Furi. From here there is access to Schwarzsee via a gondola to the right, a cable car that leads on to the Trockener Steg midstation (and then on to the Klein Matterhorn), and a new gondola, opened on 18 December 2006, links Furi to Riffelberg on the Gornergrat mountain. Travel by air! The nearest airports to Zermatt are Sion, Geneva, Zurich and Milan. Geneva airport 236 km / 2 hours 40 mins drive / 3 hours 50 mins by train and 45 minutes by helicopter charter. Zurich airport 237 km / 3 hours 50 minutes drive / 3 hours 40 mins by train. Milan Malpensa airport 197 km / 3 hours drive / 3 hours 45 mins by train. Sion airport 82km / 1 hour 30 minutes drive / 2 hours by train and less than 15 minutes by helicopter transfer. Travel to Zermatt by private jet and helicopter service. So pack your bags and grab your passport because you’re going to want to book a flight to Zermatt, Switzerland...
Switzerland VIP services
travel with pleasureZermatt, Zermatt 3920; Switzerland
ALL OVER Switzerland - Zermatt VIP services

E-mail: contact@vip-charter-service.com ; Telephone 24/7:+389 72 788 267; Zermatt
Best price range for Best VIP service offers a variety of services in Switzerland:
-
Zermatt luxury rent a car services
-
Zermatt luxury cars hire is personalized one-on-one instruction on your vehicle’s features by our trained staff.
-
Zermatt luxury car rental categories of new vehicles equipped with the latest technology.
-
Zermatt luxury rent a car 24/7 Roadside Assistance (towing, lockouts, jump-starts, and fuel-delivery)
-
-
Zermatt jet charters hire services
-
Zermatt private jet charter priority is your contentment: Fast and friendly customer service is our highest priority.
-
Once you reserve your Zermatt private jet charter flight, we can handle all ground transportation at your destination.
-
Zermatt private jet charter Empty Legs: negotiable prices based on airplane flexibility, savings of up to 75% on standard prices.
-
-
Zermatt helicopter charter flight service
-
Zermatt helicopter charter prices are unbeatable because many of the services we offer are FREE of CHARGE.
-
Zermatt helicopter charter flights, business flights to hire all over Switzerland.
-
Luxury helicopter charter from & to Zermatt - 100% privacy. Switzerland VIP helicopter service!
-
| Site Map | Terms & Conditions | Policy | Partner Links | W3C | Switzerland |
|---|

| Welcome to Switzerland |
|---|

Zermatt private jet charter
Zermatt helicopter service

Zermatt luxury cars rental













